The Princess of Wales has announced in a statement that she has been diagnosed with cancer after an incidental finding following abdominal surgery.
Kate Middleton also said she was undergoing “preventative” chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy is a term used to describe the treatment of someone diagnosed with cancer and is used to kill cancerous cells – although Kate specifically used the term preventative chemotherapy.
In a statement she said: “In January, I underwent major abdominal surgery in London and at the time, it was thought that my condition was non-cancerous.
“The surgery was successful. However, tests after the operation found cancer had been present. My medical team therefore advised that I should undergo a course of preventative chemotherapy and I am now in the early stages of that treatment.”
Follow our live blog on reaction to Kate’s cancer diagnosis by clicking here
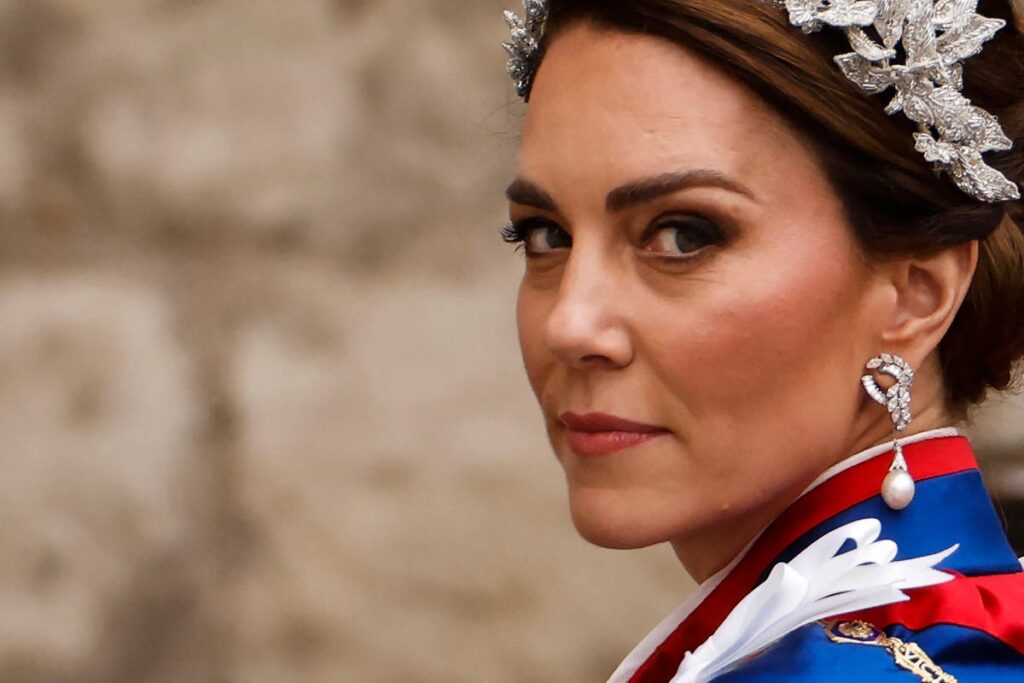
Kate announced the cancer diagnosis in a statement issued on Friday evening
(REUTERS/Hannah McKay)
What is preventative chemotherapy?
Preventative chemotherapy isn’t an official NHS term for a type of treatment and no further information has been given on Kate’s cancer, or the type of treatment she’s having.
There are current treatments that exist called “chemoprevention” which lower the risk of getting cancer, or of it returning in healthy people.
For example, it is currently used for people who have not developed breast cancer but are at increased risk of getting it due to their family history.
In 2021-22 more than 320,000 people received treatment for cancer on the NHS including chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Chemotherapy medicines are used to kill cancer cells. The drugs disrupt the way cancer cells grow and divide and therefore stop the cancer cells from spreading in the body.
According to specialists at The Royal Marsden, a cancer hospital in London, a chemotherapy called “adjuvant therapy” is sometimes used to help destroy cancer cells that may remain after surgery or radiotherapy.
Other types of chemotherapy include: neo-adjuvant therapy, which is given before surgery or radiotherapy to shrink the tumour; peri-operative therapy that is given both before and after surgery, and palliative, which is to help relieve symptoms if cancer has spread.
According to the World Health Organisation there is a public health approach called “preventive chemotherapy”, which is used on whole populations, where large-scale medicines are administered to prevent certain diseases. These include lymphatic filariasis, commonly known as elephantiasis.